Understanding a Prostate Abscess
An abscess is a pocket of infection that has liquid called pus. A pocket of infection like this in the prostate gland is called a prostate abscess.
What causes a prostate abscess?
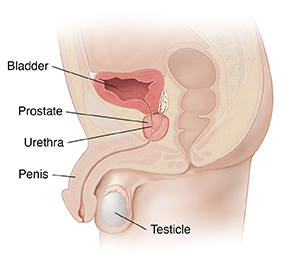
The prostate is a small gland in the lower pelvis. It's located under your bladder. The gland surrounds the urethra. This is the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. An abscess can occur if you have an infection of the prostate gland caused by bacteria (bacterial prostatitis). In some cases, prostatitis may be caused by a fungus.
If you have prostatitis, you may be at higher risk for a prostate abscess if you have any of these:
-
Diabetes that isn’t controlled well
-
Severe kidney disease
-
Liver cirrhosis
-
Weak immune system
-
Need to use a catheter to pass urine
-
An infection in your body that reaches your bloodstream (bacteremia)
-
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
-
A recent prostate biopsy
Symptoms of a prostate abscess
Symptoms can include:
-
Fever
-
Chills
-
Pain in the area between your penis and anus (perineum)
-
Pain or pressure in your rectum
-
Needing to pee often, or trouble peeing
-
Pain or burning feeling when you pee
-
Blood in your pee
-
Pain in your lower back
-
Body aches
-
Fluid leaking from the tip of the penis
Diagnosing a prostate abscess
The healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and health history. You may have a digital rectal exam. You may have tests such as:
-
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS). This test uses sound waves send through a wand put in your rectum. The sound waves create images of your body tissues on a computer screen. This test can help show if you have an abscess.
-
CT scan. This test uses a series of X-rays and a computer. You may also be given a chemical in your bloodstream to help make clearer images. This test can help show if you have an abscess.
-
Urine tests. These tests look for bacteria in your urine.
-
Blood tests. These tests can look for signs of infection.
Treatment for a prostate abscess
Types of treatment include:
-
Antibiotic medicine. You will be given medicine to kill the bacteria causing your infection. This may be done through an IV line in your arm or hand. You may need to stay in the hospital while this is done. Or you may take medicine at home. This medicine may be needed for several weeks.
-
Draining the fluid. You may also have the fluid drained from the abscess. This may be done through the skin of your groin with a needle and a thin tube (catheter). Ultrasound is used to make sure the needle and tube goes to the right spot.
-
Surgery. You may need surgery to drain and treat the abscess if it's severe. This is done with a cystoscope. This is a tool with a camera that lets the provider look inside the urethra.
Possible complications of a prostate abscess
A prostate abscess that is hard to treat can sometimes spread infection to the bloodstream. This is called bacteremia. This can cause a severe illness called sepsis, and may lead to death.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider if you have any of these:
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.